What is the Apostille Convention?
Guide to authenticating international documents
In today’s world, the Apostille Convention plays a crucial role in simplifying the process of legalizing international documents and ensuring the smooth exchange of documents between countries. Whether you are involved in international business, legal matters, or personal affairs, understanding the Apostille agreement can save you time, money, and unnecessary hassle. In this article, we will explore the Apostille agreement, its importance, and how it can benefit investors and companies around the world.
When was the Apostille Convention established?
It is an international treaty created to simplify the process of legalizing public documents for use in foreign countries. The Convention was adopted on October 5, 1961 in The Hague, Netherlands, and entered into force on January 24, 1965.
This agreement is also known as the Hague Convention for the Abolition of the Requirement for Legalization of Foreign Public Documents, and its primary purpose is to facilitate the recognition of public documents across participating countries. These public documents include birth certificates, marriage licenses, diplomas, legal rulings, and more.
What does an apostille certificate include?
An apostille certificate contains basic information, including the name of the issuing body, date of issue, signature of the authorized person, and a unique identification number. This certificate is attached to the document in question, making it valid and legally acceptable in any other country that is a member of the Convention.
What are the objectives of the Apostille Convention?
One of the main goals of the Convention is to eliminate the long and expensive process of authenticating or authenticating documents. Before the Apostille agreement, individuals and companies seeking to use foreign documents often had to go through multiple levels of certification, which could be time-consuming and often expensive.
Under the Apostille Convention, participating countries agreed to recognize the apostille as the only form of authentication required for foreign public documents. When a document is legalized, it receives a standardized certificate called an apostille, which verifies its authenticity.
What are the benefits of the Apostille Convention?
Simplified Process: One of the most important advantages of the Apostille agreement is the simplification of the document legalization process. Instead of going through complex and expensive procedures for each country, individuals and companies can use an Apostille certificate to verify their documents internationally.
Cost Savings Cost: The Apostille Convention is more economical than traditional authentication methods, which often require multiple steps and fees. With an Apostille agreement, you can save time and money.
Global Acceptance: The Apostille Convention has widespread international recognition, involving more than 120 countries. This global acceptance ensures that your documents are recognized and respected in most parts of the world.
The Apostille Convention simplifies the process of legalizing public documents for international use by providing a uniform certificate that is widely accepted among member states. This simplification reduces administrative burdens, lowers costs, and speeds up the document recognition process in foreign jurisdictions, making it a valuable tool for individuals, companies, and governments involved in international transactions and legal proceedings. The Caribbean countries are also signatories to the Apostille Convention, which greatly facilitates obtaining citizenship by investment and opens new horizons in investment.
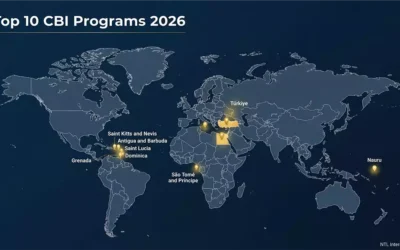
Top Citizenship by investment Programs in 2026
Top Citizenship by Investment Programs in 2026 | NTL International src="https://ntlinternational.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/ntl_top10_cbi__map.webp" alt="World map showing the top citizenship by investment programs ranked by application volume 2026, NTL...