Agriculture:
Agriculture is an essential sector in Albania. One of the earliest agricultural lands in Europe has been found in southeastern Albania.
The former governments allocated substantial resources to the development of agriculture. Large-scale programs of land reclamation, soil improvement, and irrigation, as well as increased use of fertilizers, all contributed to a significant expansion of agricultural production. Later, agriculture has registered annual growth during the latest periods.
About half of the economically active population is employed in agriculture. Only one-fourth of the total land area is arable, yet the country meets nearly all its food needs from domestic production. Albania occupies a world leading position for olive oil production. The main crops are wheat, corn, sugar beets, and watermelons. Apples, plums, grapes, walnuts, and chestnuts are also grown. Citrus fruits are cultivated on the southern coast, as are figs and olives wherever there is sufficient irrigation. Major livestock are sheep, goats, cattle, and pigs so, meat and dairy products are available, and Albania is also famous for traditional medicine, aromatic plants and honey.
Forests:
Forests cover about one-third of Albania. The country has lost much of its forest area, however, due to clearance for agriculture, pasture, and fuel wood. In the mid-1990s the Albanian government joined with Italy and the World Bank to implement a forestry project, which included the strengthening of Albania’s environmental institutions and the introduction of sustainable forestry methods.
Fishing:
The Albanian fishing industry has great potential; however, due to a lack of professional fishermen and the use of antiquated equipment, it has not been fully developed. The catch in the Ionian Sea includes carp, trout, sea bream, mussels, and crustaceans. The country’s main fishing ports are at Sarandë, Vlorë, Shëngjin, and Durrës, the last of which is the country’s largest and most important. Port facilities have also been developed on inland lakes. Family-run trout farms have increased in importance, as have shrimp farms. Anchovies imported from other Mediterranean countries are canned for export.
CBI Due Diligence Process for Second Citizenship 2026
CBI Due Diligence Process for Second Citizenship 2026 | NTL International alt="CBI due diligence process for second citizenship application - NTL compliance advisory" width="1400" height="788" loading="eager" Compliance Guide CBI Due Diligence Process for Second...
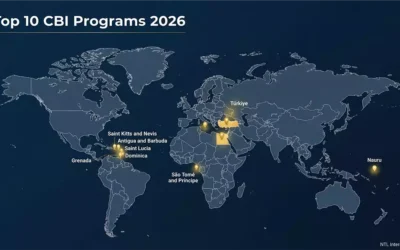
Top Citizenship by investment Programs in 2026
Top Citizenship by Investment Programs in 2026 | NTL International src="https://ntlinternational.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/ntl_top10_cbi__map.webp" alt="World map showing the top citizenship by investment programs ranked by application volume 2026, NTL...